columnar activated carbon filtration and adsorption principle
"Activated carbon is a commonly used filtering material, and columnar activated carbon, a form of activated carbon, is typically employed for filtering and absorbing pollutants in water and air. This article will commence with an exploration of the production methods of columnar activated carbon, followed by an elucidation of its filtering and adsorption principles, as well as its diverse applications."
How to Manufacture Columnar Activated Carbon
Columnar activated carbon is fabricated using activated carbon particles. One approach involves filling a plastic tube with activated carbon granules and subsequently heating it to create a dense, rotationally molded body. However, the columnar activated carbon produced through this method often exhibits a limited surface area and thus, a suboptimal filtration effect.
A more effective method involves incorporating activated carbon particles with a specific binder. The mixture is then dried at high temperatures, allowing the binder to fuse with the activated carbon particles, resulting in a columnar activated carbon with superior filtration capabilities. This process ensures a smoother flow of text and a more precise utilization of terminology.

Filtration Principle of Columnar Activated Carbon
The filtration principle of columnar activated carbon lies in physical adsorption. Physical adsorption involves the attachment of gas or liquid molecules to the surface of an adsorbent through intermolecular forces of attraction. The unique manufacturing process of columnar activated carbon creates an abundance of micropores and mesopores, enabling it to effectively adsorb various impurities. Given the minute gaps between the particles of columnar activated carbon, these impurities are unable to escape through these spaces, resulting in efficient filtration. This process ensures a highly precise and smooth operation, making columnar activated carbon an ideal choice for purification tasks.
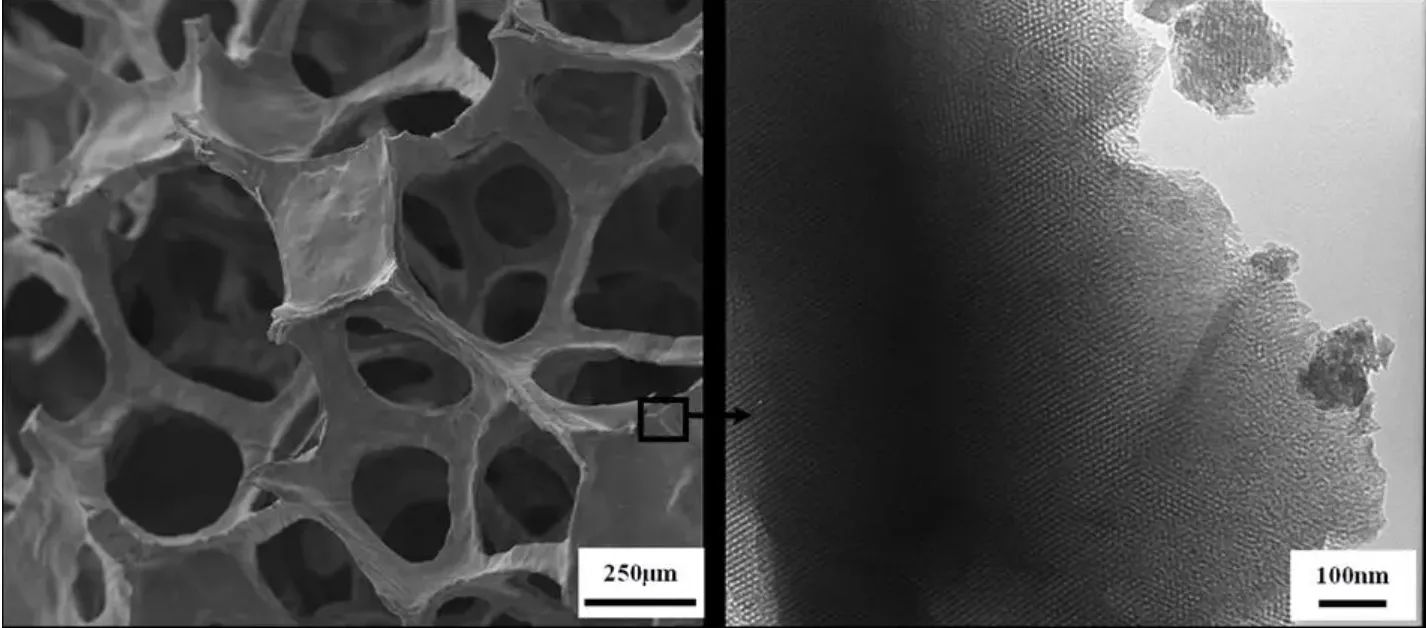
Adsorption Principle of Columnar Activated Carbon
The adsorption principle of columnar activated carbon is chemical adsorption. Chemical adsorption refers to the binding of adsorbents through chemical bonds. Due to its large surface area and porous structure, columnar activated carbon exhibits high adsorption efficiency. Various organic pollutants, such as organic compounds, chlorine, and benzene, are adsorbed and effectively removed by the columnar activated carbon.
Applications of Columnar Activated Carbon
Columnar activated carbon is widely used in air purification and water purification. In the field of water treatment and purification, activated carbon is frequently employed to remove suspended solids, organic pollutants, odors, and colors. For instance, some drinking water facilities utilize columnar activated carbon to eliminate chlorine dioxide and chloride ions from water. In air purification, columnar activated carbon is commonly applied to filter odors and harmful gases from the air. It is often used in car air purifiers to filter harmful gases such as nitrogen dioxide and formaldehyde, purifying the air.

In conclusion
The production process, along with the filtration and adsorption principles of columnar activated carbon, has been thoroughly examined. Its widespread application in water and air purification is attributable to its exceptional full-filtration capabilities and efficient adsorption properties. By emphasizing theoretical research on columnar activated carbon, optimizing production techniques, and enhancing its adsorption and filtration effects, we can effectively facilitate the advancement of its various applications.

 EN
EN
























